West Virginia is a state in the southeastern United States, one of the so-called South Atlantic states (the only state in this group that does not have access to the Atlantic Ocean). The capital and largest city is Charleston. Other major cities are Huntington, Wheeling and Morgantown. The official nickname is Mountain State. The motto is Montani Semper liberi (“Mountains are always free”).
STATE NAME
The name of the state of West Virginia, as well as the state of Virginia, of which West Virginia was previously a part, was given in honor of the Queen of England and Ireland, Elizabeth I.
It was during the reign of Elizabeth I, who never married and was therefore called “virgin Queen “(The Virgin Queen), was founded the first settlement of the British in America, from which later grew the province of Virginia, the states of Virginia and West Virginia.
GEOGRAPHY
The area of the state is 62,755 km² (41st among the states). West Virginia borders Pennsylvania to the north, Maryland and Virginia to the east, and Kentucky and Ohio to the west. The territory of West Virginia is located in the Appalachian system (the highest point is Mount Spruce Knob). The Appalachian plateau occupies about 60% of the area of the state, and in general, mountainous terrain prevails here. The largest rivers are Canova, Potomac and Monongahila. About 80% of the state is covered with forests.
CLIMATE
Most of West Virginia has a humid continental climate with hot summers and cool winters. In the southwest of the state (in the Ohio Valley) and in the east (beyond the Allegheny Mountains), the climate is hotter, subtropical, and in the mountainous regions – on the contrary, colder. In southwestern West Virginia’s largest city and state capital, Charleston, the average temperature of the coldest winter month ranges from -4°C to 6°C, and the hottest summer month ranges from 18°C to 30°C. In the northeast, in Martinsburg, in January it is usually -5°C to 5°C, and in July – from 18°C to 31°C. The city of Bluefield, which is located in the mountains in the south of the state, in winter, temperatures usually range from -3°C to 6°C, and in summer – from 18°C to 27°C.
ECONOMY
West Virginia’s main economic sectors are industry, mining, logging, tourism, and agriculture. West Virginia ranks second in the United States (after Wyoming) in terms of coal reserves and production. A significant part of it is used for the production of electricity at thermal power plants, as well as for processing into liquid fuels. In addition to coal, large deposits of natural gas have been explored in the state and, on a smaller scale, oil is being produced. In West Virginia, industry is very well developed, primarily chemical. The factories of BASF, Bayer, Dow Chemicals, DuPont produce dyes, acids, polymers, herbicides – hundreds of different types of chemicals, providing more than 40% of the state’s GDP. Also in West Virginia, metallurgical plants operate (in the northern counties, in the Wheeling area),
TOURISM
Very popular with tourists are nature reserves located in the Potomac Highlands, including the George Washington National Forest (which also stretches into neighboring Virginia and Kentucky), the Seneca Rocks National Recreation Area (a high rock that attracts climbers), Lost River State Parks, Berkeley Springs (famous for its mineral springs) and others.
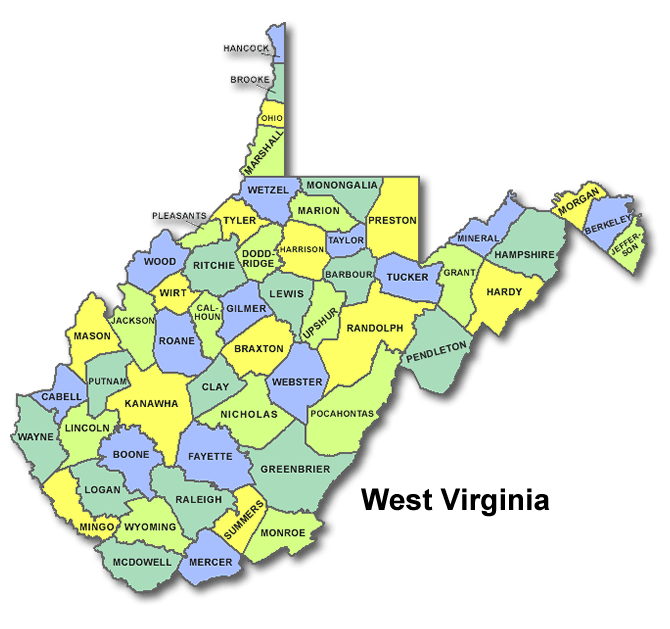
Largest Counties in West Virginia
West Virginia separated from Virginia during the Civil War and became a state in 1863. It is known for its coal mining and Appalachian culture. West Virginia has 55 counties. 10 Largest Counties in West Virginia 1. Kanawha County County…
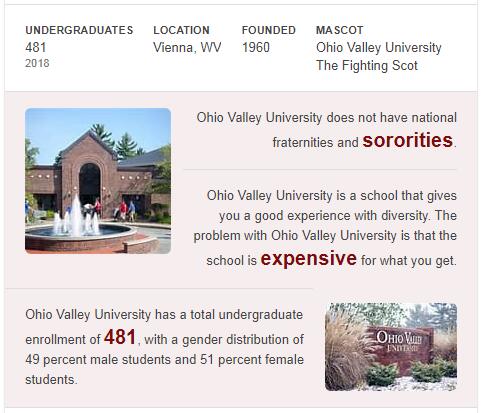
Read more